Key Takeaways
- Edge computing enhances IoT by processing data near the source.
- Real-time processing minimizes latency and optimizes bandwidth.
- Local data processing strengthens security and reduces cloud reliance.
- Improved reliability ensures consistent IoT performance.
- Cost-effective solution for scalable IoT deployments.
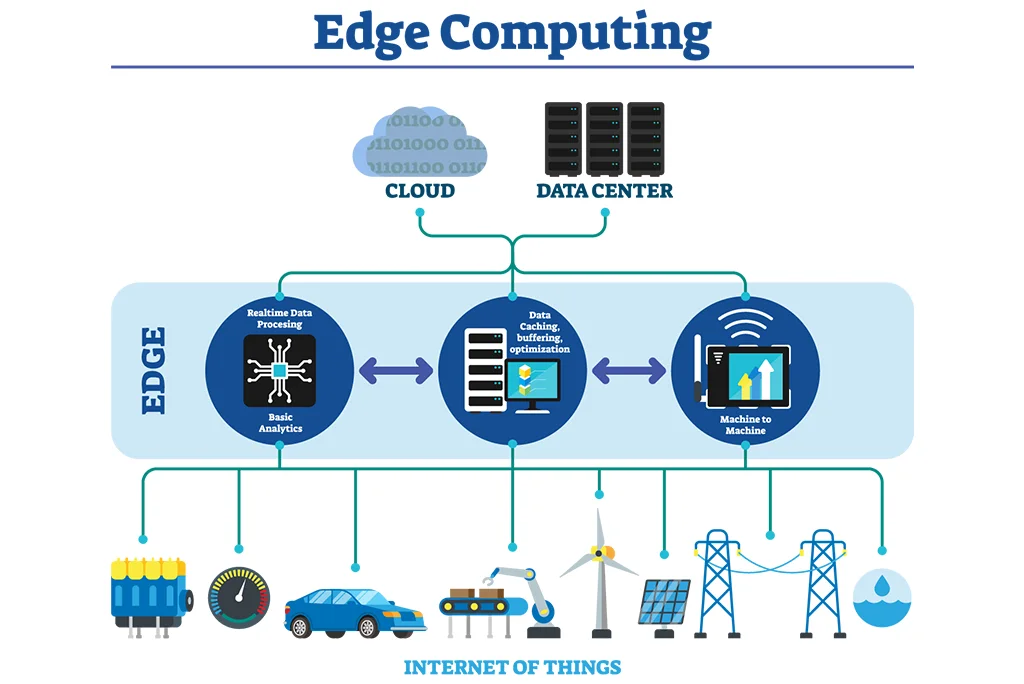
Introduction to Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing is reshaping the Internet of Things (IoT) by enabling data processing closer to devices. This approach reduces latency, lowers bandwidth costs, and enhances security, making it ideal for modern IoT systems. By decentralizing computation, edge computing addresses the limitations of traditional cloud-based models, offering faster, more secure, and reliable IoT deployments. This article explores the transformative impact of edge computing on IoT, highlighting its benefits, components, strategies, and real-world applications.
The Evolution of IoT Data Processing
Traditional vs. Edge Computing Approaches
Traditional Cloud Computing
- Centralized processing: All data is sent to a central cloud server.
- Higher latency: Data travel time increases response delays.
- Bandwidth costs: Transmitting large data volumes is expensive.
- Single point of failure: Cloud outages disrupt operations.
- Limited offline capabilities: Requires constant internet connectivity.
Edge Computing Benefits
- Local processing: Data is processed at or near the source.
- Low latency: Faster response times for real-time applications.
- Reduced bandwidth: Minimizes data sent to the cloud.
- Enhanced reliability: Operates independently of cloud connectivity.
- Offline functionality: Supports IoT in disconnected environments.
Key Components of Edge-IoT Systems
1. Edge Devices
Edge devices are the backbone of IoT systems, enabling local data collection and processing. Key components include:
- IoT sensors and actuators: Collect and act on environmental data.
- Edge gateways: Facilitate communication between devices and networks.
- Local processing units: Handle computations on-site.
- Storage systems: Store data temporarily for processing.
- Network interfaces: Ensure connectivity with other systems.
2. Edge Software Stack
The software stack supports efficient edge operations. Critical elements include:
- Edge operating systems: Lightweight OS for resource-constrained devices.
- Container platforms: Enable scalable application deployment.
- AI/ML frameworks: Support real-time analytics and decision-making.
- Security protocols: Protect data and devices.
- Management tools: Monitor and optimize edge systems.
Implementation Strategies
1. Device Selection
Selecting the right edge devices is critical for IoT success. Consider:
- Processing power: Match device capabilities to workload demands.
- Power constraints: Opt for energy-efficient devices.
- Environmental conditions: Ensure durability in harsh settings.
- Cost considerations: Balance performance with budget.
- Scalability: Choose devices that support future growth.
2. Network Architecture
A robust network architecture ensures seamless edge operations. Key considerations:
- Local topology: Design efficient local networks for data flow.
- Cloud connectivity: Enable selective data transfer to the cloud.
- Data synchronization: Maintain consistency across edge and cloud.
- Security protocols: Protect data during transmission.
- Failover mechanisms: Ensure uptime during network disruptions.
Security Considerations
1. Data Protection
Edge computing enhances IoT security by processing data locally, reducing exposure to external threats. Key measures:
- End-to-end encryption: Secure data at rest and in transit.
- Access control: Restrict device and data access.
- Secure boot: Prevent unauthorized firmware changes.
- Regular updates: Patch vulnerabilities promptly.
- Threat detection: Monitor for suspicious activity.
2. Network Security
Protecting the edge network is vital for IoT integrity. Implement:
- Firewall implementation: Block unauthorized access.
- VPN connections: Secure remote communications.
- Intrusion detection: Identify and mitigate threats.
- Traffic monitoring: Analyze network activity for anomalies.
- Security policies: Enforce consistent security standards.
Performance Optimization
1. Resource Management
Optimizing edge resources enhances efficiency. Strategies include:
- Load balancing: Distribute tasks across devices.
- Cache management: Store frequently accessed data locally.
- Power optimization: Reduce energy consumption.
- Storage management: Prioritize critical data storage.
- Network optimization: Minimize data transmission overhead.
2. Data Processing
Efficient data handling improves edge performance. Techniques include:
- Data filtering: Process only relevant data.
- Compression: Reduce data size for faster transmission.
- Batch processing: Group data for efficient handling.
- Real-time analytics: Enable immediate insights.
- Data prioritization: Focus on critical data first.
Real-World Applications
Case Study: Smart Manufacturing
A manufacturing plant implemented edge computing, achieving:
- 60% latency reduction: Faster decision-making on the factory floor.
- 40% bandwidth savings: Reduced cloud data transfers.
- Improved efficiency: Streamlined production processes.
- Enhanced quality control: Real-time defect detection.
- Better predictive maintenance: Anticipated equipment failures.
Future Trends
Edge computing continues to evolve, with trends shaping IoT:
- AI at the edge: Enables smarter, autonomous devices.
- 5G integration: Enhances connectivity and speed.
- Advanced security: Strengthens IoT protections.
- Autonomous systems: Supports self-managing IoT networks.
- Edge-native applications: Designed specifically for edge environments.
FAQ
What are the main benefits of edge computing for IoT?
Edge computing reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, enhances security, and improves reliability, making IoT systems more efficient and resilient.
How does edge computing improve IoT security?
By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes data exposure to external networks, reducing risks of breaches and unauthorized access.
What should organizations consider when implementing edge computing?
Evaluate device capabilities, network architecture, security needs, and scalability to ensure a robust and future-proof IoT deployment.

Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming IoT by enabling faster, more secure, and cost-effective data processing. By decentralizing computation, organizations can overcome the limitations of traditional cloud models, unlocking new possibilities for IoT applications.
Next Steps
To adopt edge computing for IoT:
- Assess IoT requirements and goals.
- Evaluate edge computing solutions and vendors.
- Plan network architecture and security measures.
- Test and deploy edge systems systematically.
For more insights, explore our Edge Computing section.


