Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive IoT Security: Robust measures are essential for device and network protection.
- Privacy First: Addressing data privacy concerns ensures user trust.
- 5G Security Needs: Enhanced protocols are critical for secure connectivity.
- Strategic Implementation: Careful planning mitigates risks effectively.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular audits maintain system integrity.
Introduction to IoT Security and Privacy
As Internet of Things (IoT) devices proliferate, security and privacy challenges intensify, particularly with the advent of 5G networks. The synergy between 5G and IoT enables unprecedented connectivity, but it also amplifies risks. This article delves into the complexities of IoT security and privacy, offering strategies to safeguard systems and data in this interconnected landscape.
Understanding IoT Security Challenges
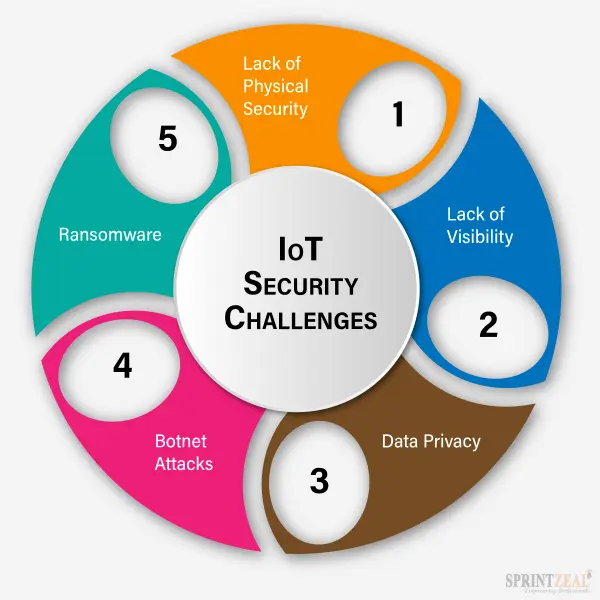
1. Core Security Challenges
IoT ecosystems face multifaceted challenges:
- Device Security: Ensuring devices resist tampering and unauthorized access.
- Network Protection: Securing communication channels against intrusions.
- Data Privacy: Safeguarding sensitive information from breaches.
- Access Control: Managing permissions to prevent misuse.
- Compliance Requirements: Adhering to regulatory standards like GDPR.
2. Primary Security Risks
Key risks threatening IoT systems include:
- Unauthorized Access: Hackers exploiting weak authentication.
- Data Breaches: Exposure of sensitive user information.
- Device Tampering: Physical or software-based manipulation.
- Network Attacks: Exploits like DDoS targeting connectivity.
- Privacy Violations: Unauthorized data collection or sharing.
Implementation Strategies for IoT Security
1. Robust Security Framework
A comprehensive framework is vital:
- Security Policies: Define clear guidelines for device and data management.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access to limit exposure.
- Monitoring Systems: Deploy real-time threat detection tools.
- Incident Response: Establish protocols for rapid response to breaches.
- Compliance Measures: Ensure alignment with industry regulations.
2. Privacy Protection Measures
Protecting user privacy involves:
- Data Encryption: Secure data at rest and in transit.
- Privacy Policies: Transparent guidelines on data usage.
- User Consent: Obtain explicit permission for data collection.
- Data Minimization: Collect only essential data.
- Access Controls: Restrict data access to authorized personnel.
Technical Considerations for Secure IoT
1. Device Security Protocols
Devices must incorporate:
- Authentication: Multi-factor authentication for access.
- Encryption: End-to-end encryption for data security.
- Firmware Updates: Regular patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Access Control: Restrict device access to authorized users.
- Monitoring: Continuous tracking of device behavior.
2. Network Security Essentials
Network protection requires:
- Segmentation: Isolate IoT devices to limit breach spread.
- Encryption: Secure communication channels.
- Access Control: Restrict network access to verified devices.
- Monitoring: Detect anomalies in network traffic.
- Incident Response: Swiftly address network threats.
Best Practices for IoT Security and Privacy
1. Security Best Practices
Adopt these guidelines:
- Regular Updates: Keep firmware and software current.
- Strong Authentication: Use complex passwords and biometrics.
- Encryption: Protect data with advanced algorithms.
- Access Control: Limit permissions to essential users.
- Monitoring: Use AI-driven tools for threat detection.
2. Privacy Best Practices
Implement privacy controls:
- Data Protection: Encrypt sensitive information.
- User Consent: Ensure transparent data collection processes.
- Access Management: Restrict data access to authorized roles.
- Data Minimization: Reduce data collection to necessities.
- Regular Audits: Verify compliance with privacy standards.
IoT Security Use Cases
1. Security Applications
IoT security solutions include:
- Device Protection: Safeguarding endpoints from tampering.
- Network Security: Preventing unauthorized network access.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring secure data handling.
- Access Control: Managing user permissions.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory standards.
2. Industry-Specific Solutions
IoT security benefits various sectors:
- Manufacturing: Securing automated production lines.
- Healthcare: Protecting patient data and medical devices.
- Transportation: Ensuring secure vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
- Energy: Safeguarding smart grids from cyberattacks.
- Smart Cities: Enhancing privacy in urban IoT systems.
Implementation Challenges
1. Technical Challenges
Deploying IoT security faces:
- Device Diversity: Varying standards across devices.
- Network Complexity: Managing large-scale connectivity.
- Security Requirements: Balancing usability and protection.
- Privacy Concerns: Addressing user data concerns.
- Compliance Needs: Navigating global regulations.
2. Operational Challenges
Operational hurdles include:
- Cost Management: Budgeting for security infrastructure.
- Resource Allocation: Deploying skilled personnel.
- Team Training: Educating staff on IoT security.
- Maintenance: Ensuring ongoing system updates.
- Monitoring: Sustaining vigilant oversight.
Case Study: Industrial IoT Security Success
An industrial facility implemented a robust IoT security framework, achieving:
- 90% Incident Reduction: Minimized security breaches.
- 70% Cost Savings: Optimized security investments.
- Improved Compliance: Met stringent regulatory standards.
- Enhanced Security: Strengthened device and network protections.
- Better Privacy: Safeguarded sensitive operational data.
Future Trends in IoT Security
Emerging trends shaping IoT security:
- Advanced Security Protocols: Next-gen encryption methods.
- AI-Driven Protection: Machine learning for threat detection.
- Enhanced Privacy Measures: Stronger user data protections.
- Improved Monitoring Tools: Real-time analytics for IoT systems.
- Streamlined Compliance: Automated regulatory adherence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main IoT security challenges?
Device security, network protection, data privacy, access control, and compliance are critical challenges.
How can organizations secure IoT systems?
Implement robust security frameworks, regular monitoring, and privacy-first policies.
What are key IoT privacy concerns?
Data protection, user consent, access management, and data minimization are top concerns.
Conclusion
IoT security and privacy are paramount in the 5G era. By adopting best practices, addressing technical and operational challenges, and leveraging emerging trends, organizations can build secure, private, and reliable IoT ecosystems.

Next Steps for IoT Security
To enhance your IoT security:
- Develop comprehensive security policies.
- Implement robust protection measures.
- Establish continuous monitoring systems.
- Conduct regular privacy and security audits.