Overview
Modern data platform architectures have become the essential foundation for enabling real-time analytics, scalable storage, and advanced business intelligence across enterprises today. These unified systems ingest, process, store, analyze, and govern data from diverse sources, supporting seamless integration with cloud and hybrid environments. In a data-driven economy, building a scalable, efficient, and flexible data platform has evolved into a necessity rather than a luxury. This guide provides an in-depth look into the core components, architectural patterns, best practices, and emerging trends shaping data platforms in 2025.
What Is a Modern Data Platform?
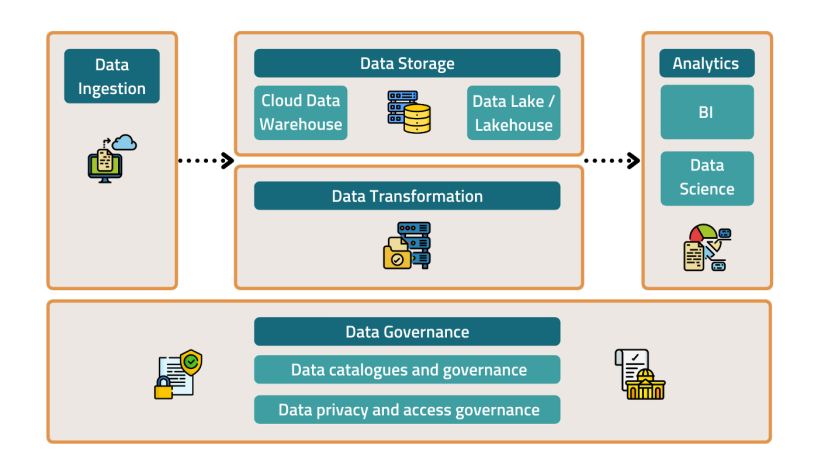
A modern data platform is a unified ecosystem designed to manage the entire data lifecycle—from ingestion through processing to analytics and governance. Unlike legacy systems that often rely on siloed batch processes, modern data platforms handle both batch and real-time streaming data at scale. They support business intelligence (BI), machine learning (ML), and provide metadata-driven governance frameworks to ensure data quality, security, and compliance. Cloud-native platforms leverage separation of compute and storage for flexible scalability, adopting lakehouse and hybrid architectures that unify the benefits of data lakes and warehouses.
Core Components
- Data Ingestion
Modern platforms support hybrid ingestion methods including batch processing for historical or large-scale data and real-time streaming ingestion for immediate decision-making scenarios, such as fraud detection or personalization. Tools enable extraction from diverse sources including transactional databases, SaaS applications, clickstreams, and third-party APIs. - Storage
Storage infrastructure includes data lakes, warehouses, and lakehouses that store raw, curated, and processed data in layered zones. Scalability is achieved via distributed cloud storage solutions like Snowflake, Databricks, and Google BigQuery, allowing separation of compute and storage to optimize costs and performance. - Processing and Transformation
Data transformation pipelines utilize ETL (Extract-Transform-Load) or ELT (Extract-Load-Transform) frameworks for cleaning, validating, and enriching data. Workflow orchestration automates these pipelines while maintaining data lineage and quality controls. Streaming and batch processing coexist to serve diverse analytics workloads. - Analytics and Intelligence
Business intelligence tools enable self-service analytics, real-time dashboards, predictive modeling, and KPI tracking. Increasingly, AI-powered insights are embedded to automate anomaly detection, decision support, and advanced forecasting, making platforms more proactive. - Data Governance and Security
Essential governance layers enforce role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, compliance auditing, and metadata management. Data observability tools monitor platform health, data quality, and pipeline reliability to ensure trustworthiness.
Architecture Design Patterns
- Layered Architecture
A well-structured platform breaks down into ingestion, storage, processing, analytics, and governance layers, each with distinct roles but integrated through APIs and event-driven workflows. - Microservices and Modularization
Decoupled, containerized microservices provide flexibility, enabling independent scaling, easy upgrades, and composability. This modular approach aligns with modern DevOps and CI/CD pipelines to accelerate delivery. - Data Mesh and Federated Ownership
Organizations adopt decentralized data ownership models where domain teams manage their datasets as products, supported by platform self-service capabilities. This approach fosters scalability, accountability, and better alignment with business functions.
Best Practices for Scalability, Security, and Performance
- Scalability & Performance
Distribute storage and compute, implement partitioning and caching, optimize queries with indexing, and leverage cloud-native auto-scaling features to handle growing data volumes efficiently. - Security & Compliance
Employ encryption at rest and in transit, enforce RBAC, automate compliance checks, conduct regular audits, and integrate security monitoring into pipelines. - Data Quality & Governance
Implement data validation early, manage metadata actively, track lineage for traceability, appoint data stewards, and regularly update governance policies.
Real-World Use Cases
- Business Intelligence
Real-time dashboards, predictive analytics, self-service reporting, and executive KPIs empower data-driven decisions and agile business responses. - Industry-Specific Applications
- Healthcare: patient analytics, integrating clinical data for improved care
- Finance: fraud detection, risk analysis with real-time alerts
- Retail: customer behavior insights, inventory optimization
- Manufacturing: IoT data analytics, process automation for efficiency
Industry Trends (2023-2025)
- Data Mesh: Federated, domain-driven data ownership gaining adoption for scalability and agility.
- AI-Driven Analytics: Automated insights and anomaly detection embedded in every analytics layer.
- Serverless Data Platforms: Elastic scaling with less operational overhead.
- Composable Architectures: API-driven modular components allowing flexible data platform customization.
- Enhanced Data Observability: Real-time monitoring to anticipate and prevent data pipeline failures.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Data Integration Complexity mitigated by robust connectors and standard APIs.
- Balancing Cost and Performance with elastic resources and cloud-native optimization.
- Governance at Scale demands automation and policy enforcement frameworks.
- Ensuring Data Quality through continuous validation and observability.
- Team Enablement requires fostering self-service culture and training.

Conclusion and Next Steps
Modern data platform architectures are now mission-critical enablers for data-driven enterprises. By embracing modular, cloud-native, and AI-integrated designs, organizations unlock agility, control, and actionable insights at unprecedented scale. To future-proof data platforms, it’s essential to prioritize scalability, security, automation, and strong governance frameworks.
Businesses should evaluate their current architectures, adopt flexible tools, invest in data observability, and empower teams with self-service capabilities to realize the full potential of modern data platforms.