Event-driven architecture and serverless computing have become two of the most transformative forces in modern application development. When these two paradigms are combined, organizations can build scalable, decoupled, and resilient systems that respond to real-time events with efficiency and agility. This guide explores the design patterns, benefits, challenges, and best practices of event-driven design in serverless applications, providing both conceptual foundations and actionable insights.
Why Event-Driven Fits Serverless
Serverless architecture thrives on the principle of running functions only when triggered. Event-driven design complements this perfectly because an event becomes the natural trigger. Whether it’s a user action, a system-generated message, or a data stream, events can initiate serverless functions that scale automatically. Unlike monolithic designs that rely on tightly coupled logic, event-driven patterns allow teams to decouple services, improving system reliability, flexibility, and performance.
Core Event-Driven Patterns
Several foundational event-driven design patterns are used in serverless systems:
- Event Sourcing
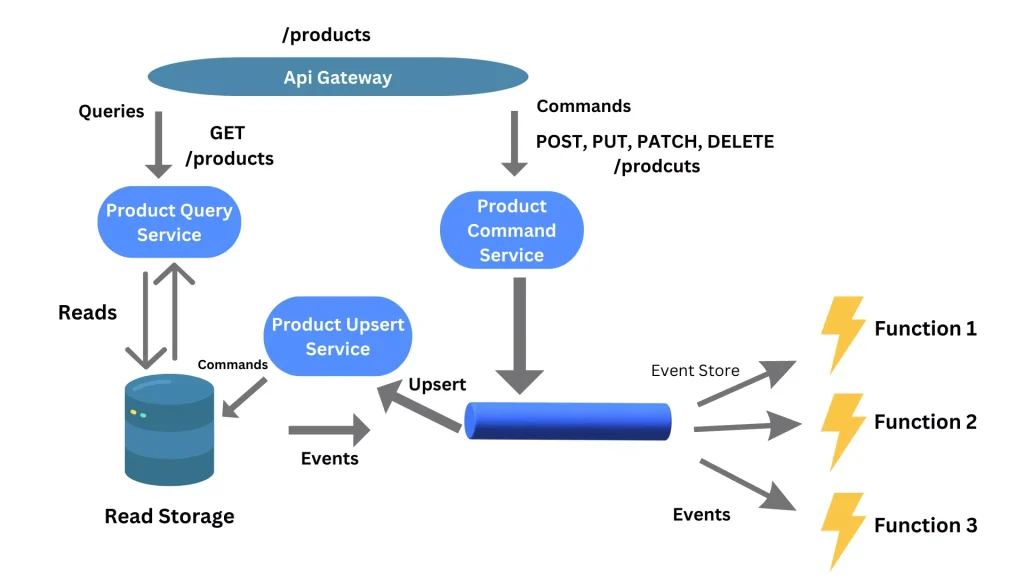
Events capture every state change as an immutable record. This pattern ensures transparency, simplifies state reconstruction, and supports compliance and auditing. - CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
Separating read and write operations improves scalability. Queries can be optimized independently while commands focus on state mutations. - Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub)
Producers publish events to a topic or bus, and consumers subscribe based on interest. This decoupling boosts flexibility and allows for scaling specific consumers independently. - Event Streaming
Continuous event streams, such as those from IoT devices or financial systems, enable real-time analytics and trigger automated responses. - Saga Pattern
Useful for long-running business processes, sagas manage distributed transactions through orchestrated or choreographed events.
Benefits of Event-Driven Serverless
The adoption of an event-driven serverless approach brings numerous advantages:
- Loose Coupling – Services communicate via events rather than direct calls, improving resilience.
- Scalability – Functions and consumers scale dynamically with event volume.
- Resilience – Failures in one component don’t bring down the entire system.
- Flexibility – Easy to add new consumers without affecting existing flows.
- Maintainability – Clear event logs simplify debugging and auditing.
Implementation Strategies
Event Design
Carefully design your events with structure, versioning, and schema validation. Consider naming conventions, event payload consistency, and backward compatibility.
Architecture Setup
Core requirements include configuring an event bus, integrating serverless functions with messaging services, setting up monitoring pipelines, and defining error handling strategies like retries and dead letter queues.
Integration Patterns
Serverless event processing commonly leverages:
- API Gateway triggers for HTTP requests
- Message queues for asynchronous decoupling
- Event streaming platforms for large-scale analytics
- Direct service integration
- Storage triggers for file or database events
Technical Considerations
When processing events, teams must handle:
- Validation – Ensuring schema integrity before storage or processing.
- Routing – Sending events to the rightful consumer service.
- Error Handling – Using retry policies and fallback mechanisms.
- Dead Letter Queues – Capturing failed events for post-mortem analysis.
Performance can be further optimized via caching, batching events, and dynamically allocating resources based on stream volumes.
Best Practices
- Clear Event Naming – Standardize naming to avoid confusion.
- Schema Validation – Promote quality and maintainability.
- Version Control – Introduce versioned fields to support evolution.
- Comprehensive Documentation – Ensure all services understand the event format and purpose.
- Testing Strategy – Include automated tests for event flows and failure scenarios.
Use Cases and Enterprise Solutions
Event-driven serverless design has practical applications across industries:
- Real-Time Processing – Financial tickers, online gaming, live dashboards.
- Data Synchronization – Keeping multiple databases consistent.
- Workflow Automation – Customer onboarding, e-commerce order handling.
- Notification Systems – Push/email notifications driven by events.
- Analytics Processing – Building data pipelines with immediate insights.
- IoT Processing – Handling millions of sensor events in distributed systems.
Enterprises also rely on event-driven serverless platforms for business workflows, integration systems, and microservices orchestration, highlighting its adaptability.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite its advantages, event-driven serverless design presents challenges:
- Technical – Event ordering, state management, and complex monitoring.
- Operational – Cost management in high-throughput systems, ensuring security and compliance, and maintaining visibility into asynchronous workflows.
- Team Training – Engineers need a shift in mindset away from synchronous architectures.
Case Study: Real-Time Analytics Success
A data analytics platform adopted an event-driven serverless architecture and achieved:
- 50% faster event processing
- 40% reduction in infrastructure costs
- Significant gains in scalability and resiliency
- Enhanced monitoring through centralized event logs
Future Outlook
The evolution of event-driven patterns in serverless systems is far from complete. Emerging directions include:
- Integration of AI/ML models for smarter event processing
- Multi-cloud support for broader deployment flexibility
- Advanced monitoring tools with AI-driven insights
- Stronger event security mechanisms
- Combining edge computing with serverless to bring event processing closer to devices

Conclusion
Event-driven design patterns, when combined with serverless architecture, offer a powerful way to build modern applications that meet the demands of scalability, speed, and resilience. By focusing on event design, careful integration, best practices, and proactive handling of challenges, organizations can unlock significant advantages and maintain a competitive edge in the digital era.
If you are ready to start, consider:
- Planning your event architecture
- Designing robust event flows
- Establishing monitoring and error handling
- Continuously refining based on best practices
For further insights, explore resources in the serverless architecture domain and keep pace with event-driven trends shaping the future of application development.